GM Automatic Transmissions
With so many transmission options available, how do you choose the right transmission? You can go with an old-school two-speed Hydra-Matic or all the new to a new-school eight-speed. Each one has it’s pros and cons from being simple to complex, cheap to expensive.
How you choose is going to vary depending on several factors. Your budget plans with the car, and skill set. A basic two-speed will fit into just about anything, while the modern eight-speeds will require tunnel surgery to fit into most classics.
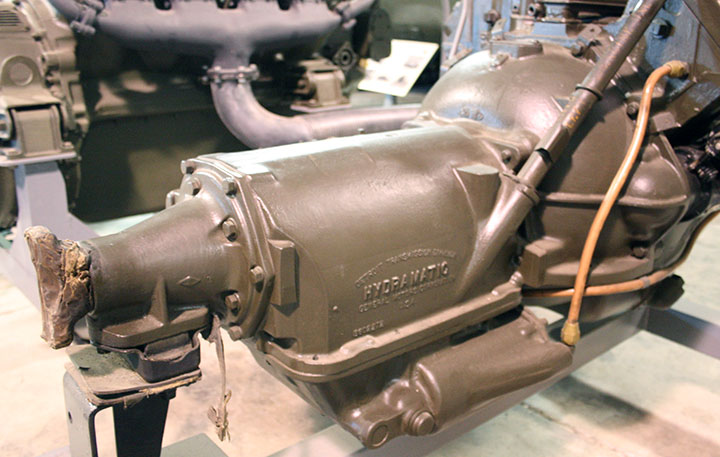
1. Hydra-Matic Transmission (1940s-1960s)
Pros:
- Revolutionary Design: The Hydra-Matic was the world’s first mass-produced automatic transmission, and it set a new standard for convenience by eliminating the need for manual shifting.
- Durability: Known for its robust construction, the Hydra-Matic was praised for its longevity and reliability in everyday use.
- Smooth Shifting: This transmission offered smoother gear changes than manual gearboxes of the time, enhancing driver comfort.
Cons:
- Complexity: The Hydra-Matic was mechanically complex, making it expensive to produce and repair, which could be a drawback for owners if something went wrong.
- Fuel Efficiency: Early Hydra-Matics were not particularly fuel-efficient due to their design, which included fewer gears and more internal friction compared to later transmissions.
- Performance: Acceleration and responsiveness were somewhat sluggish, which didn’t appeal to performance enthusiasts who preferred more direct control.
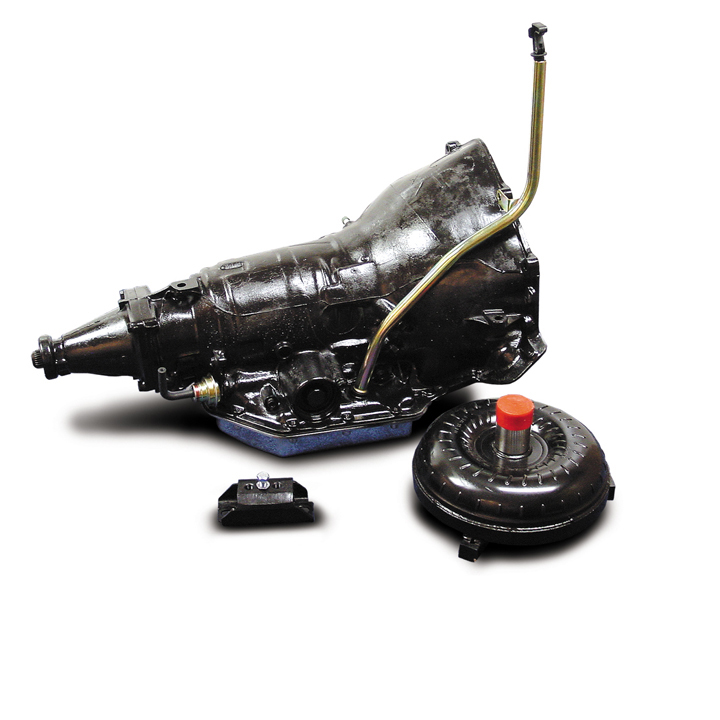
2. Turbo-Hydramatic 350 Transmission (1969-1984)
Pros:
- Reliability: The Turbo-Hydramatic 350 (TH350) earned a reputation for being one of the most reliable transmissions of its time, commonly used in a variety of GM vehicles.
- Versatility: The TH350 was versatile, fitting everything from small cars to heavy-duty trucks, making it one of GM’s most widely used transmissions.
- Performance: With quicker and more responsive shifting than earlier automatics, the TH350 was well-regarded among performance car enthusiasts.

Cons:
- Limited Gear Ratios: The TH350 was a 3-speed transmission, which limited its ability to optimize fuel efficiency and performance compared to later multi-speed automatics.
- Weight: The transmission was relatively heavy, which could impact vehicle performance and fuel economy, especially in smaller cars.
- Maintenance Costs: While reliable, the TH350 still required regular maintenance, and repairs could be costly due to the complexity of the transmission.
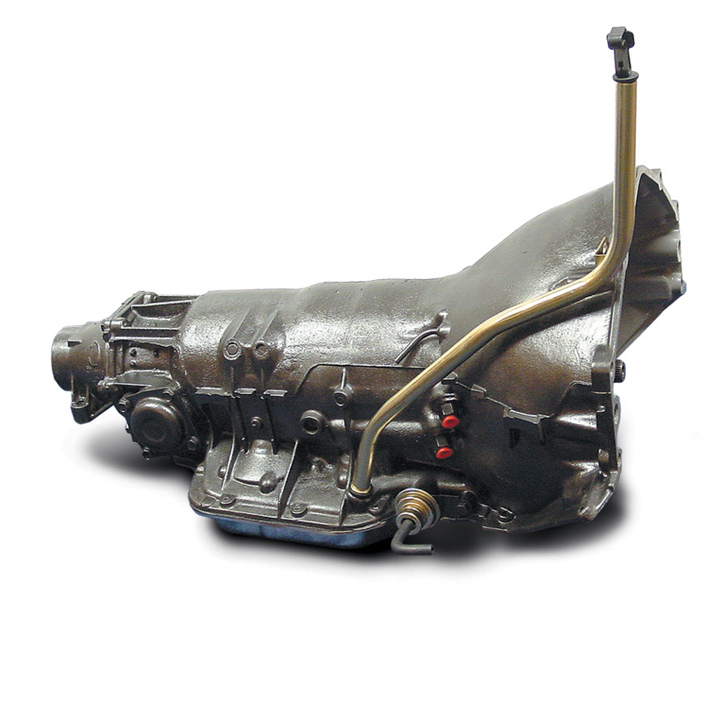
3. Turbo-Hydramatic 400 Transmission (1964-1990)
Pros:
- Heavy-Duty Capability: The Turbo-Hydramatic 400 (TH400) was designed for high-power applications, making it ideal for muscle cars, trucks, and heavy-duty vehicles.
- Durability: The TH400 is renowned for its exceptional durability, often lasting hundreds of thousands of miles without major issues.
- Smooth Power Delivery: This transmission provides a very smooth transfer of power, making it ideal for both performance and comfort-oriented vehicles.

Cons:
- Fuel Efficiency: Like other transmissions of its era, the TH400 was not optimized for fuel efficiency, which became a more significant issue as fuel prices rose.
- Weight and Size: The TH400 was larger and heavier than many other transmissions, which could negatively affect the overall performance and handling of the vehicles in which it was installed.
- Cost: The TH400 was expensive to produce and repair, and while durable, it was costly to maintain compared to lighter-duty transmissions.
4. 700R4/4L60 Transmission (1982-1992/1993-2014)
Pros:
- Overdrive Gear: The introduction of an overdrive gear in the 700R4 and its successor, the 4L60, significantly improved fuel efficiency, especially during highway driving.
- Versatility: These transmissions were highly versatile, and used in a wide range of GM vehicles, from passenger cars to trucks and SUVs.
- Improved Performance: The 700R4/4L60 offered better acceleration and overall performance, making them popular choices in the performance and off-road communities.
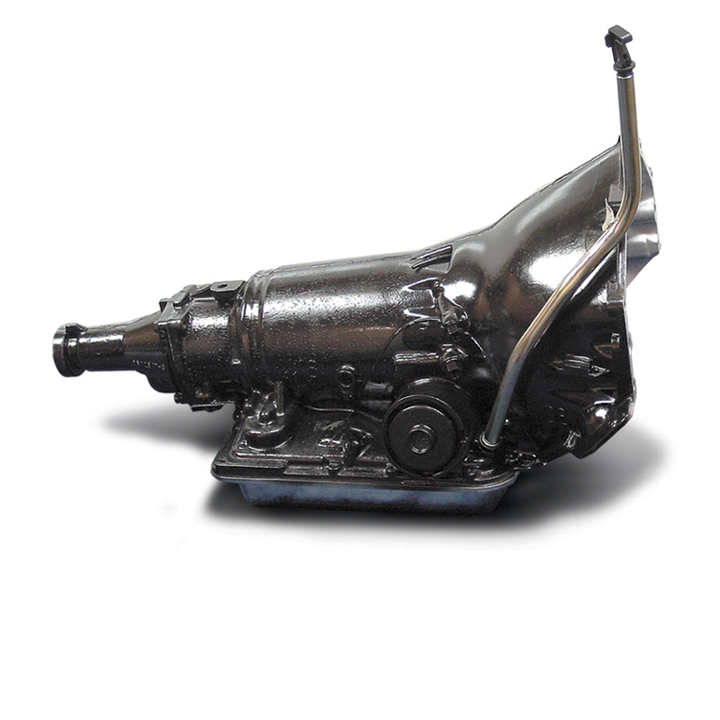

Cons:
- Early Reliability Issues: The early versions of the 700R4 were prone to failure, particularly in heavy-duty applications, though many of these issues were addressed in later models.
- Maintenance Requirements: These transmissions require regular maintenance, and failure to keep up with service intervals could lead to expensive repairs.
- Shift Quality: Some drivers reported inconsistent shift quality, particularly under heavy load or in performance settings, which could detract from the driving experience.
5. 6L80/6L90 Transmission (2006-Present)
Pros:
- Advanced Gear Ratios: The 6L80 and 6L90 transmissions feature 6 speeds, allowing for improved fuel efficiency and performance compared to older 3- and 4-speed automatics.
- Electronic Control: These transmissions are electronically controlled, which allows for precise gear shifts and the ability to adapt to different driving conditions and styles.
- Durability: Built for modern vehicles, the 6L80 and 6L90 are known for their durability, handling high torque and power outputs with ease.
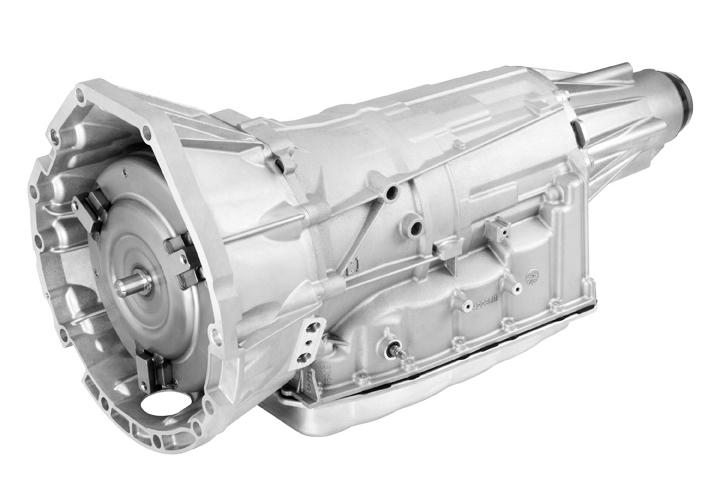

Cons:
- Complexity: The electronic systems in these transmissions can be prone to software issues, leading to shifting problems that require specialized repair.
- Cost: Repairing or replacing a 6L80 or 6L90 can be expensive due to their complexity and the need for specialized knowledge and tools.
- Weight: While more efficient than older models, these transmissions are still relatively heavy, which can slightly impact the vehicle’s overall performance and fuel economy.
6. 8L90 Transmission (2014-Present)
Pros:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: With 8 speeds, the 8L90 offers better fuel efficiency and performance than its 6-speed predecessors, particularly at highway speeds.
- Smooth Shifting: The 8L90 is designed for smooth, quick shifts, providing a refined driving experience in both luxury and performance vehicles.
- Performance Capability: This transmission can handle high levels of torque, making it suitable for performance cars and trucks.
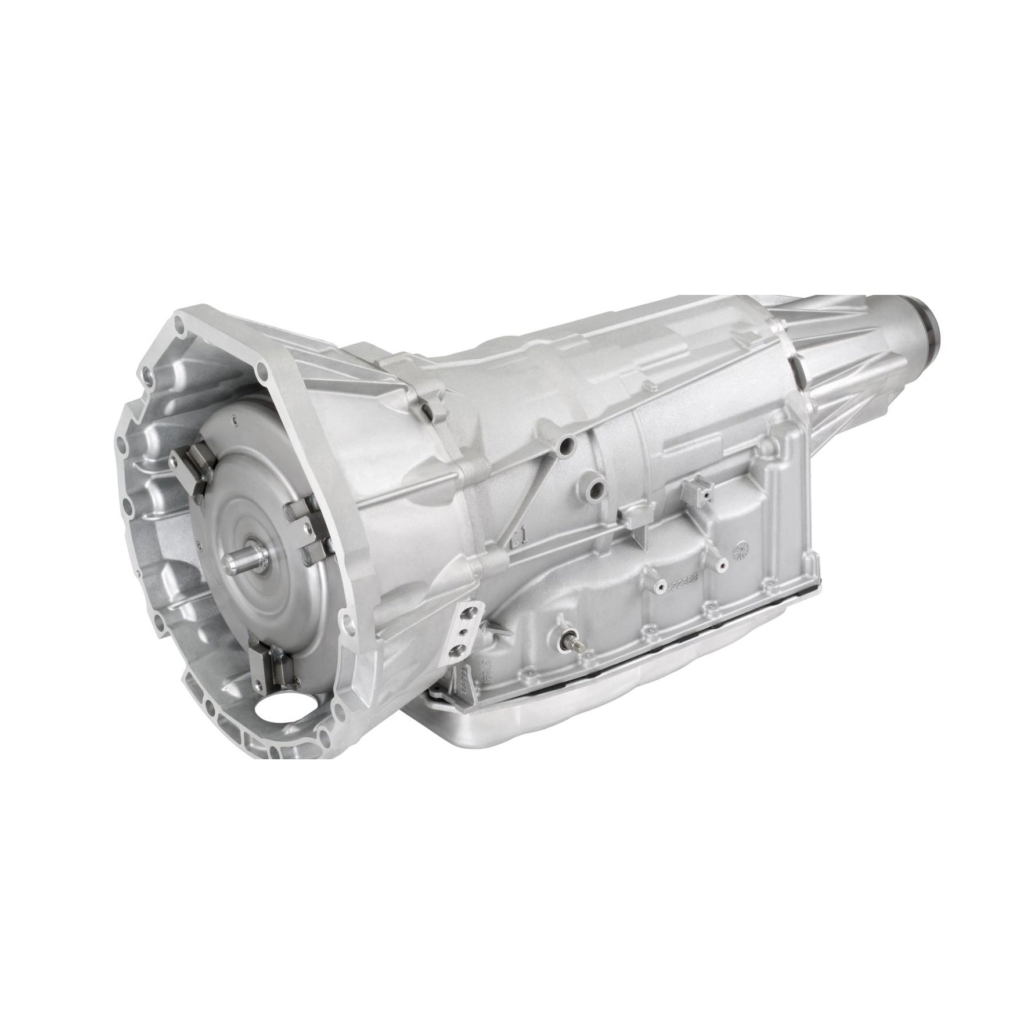

Cons:
- Complexity and Cost: The 8L90 is highly complex, making repairs and maintenance more expensive than older, simpler transmissions.
- Early Software Issues: Some early models experienced software-related shifting issues, though these have been addressed in newer versions.
- Driver Feedback: Some drivers feel that the 8-speed transmission, while efficient, can sometimes feel disconnected from the driving experience due to its focus on smoothness and efficiency.
GM’s automatic transmissions have evolved significantly over the years, each bringing its own set of advantages and challenges. From the groundbreaking Hydra-Matic to the advanced 8L90, GM has continually pushed the boundaries of transmission technology. While each transmission has had its strengths, issues such as complexity, cost, and reliability have been recurring challenges. As GM continues to innovate, the balance between performance, efficiency, and driver engagement remains a key focus in their transmission development.
For most of these transmissions, we sell them complete and ready to go. Hop on SS396.com to see the full line of transmissions or give our friendly techs a call at (203) 235-1200!