Rearend Differential Gear Ratios
Rearends, or Gear Differentials, play a big part in any rear-wheel-drive vehicle. They take the power from the engine and put it to the wheels. As with any system on a car, the more you dive into them the more technology you realize is there. Rearends are no different, there’s a lot more going on there than meets the naked eye.
One of the biggest decisions with rearends is picking the gear ratio. The gear ratio has a huge impact on how the car drives from being a quarter mile bruiser or a highway cruiser.

Understanding the Rearend Differential
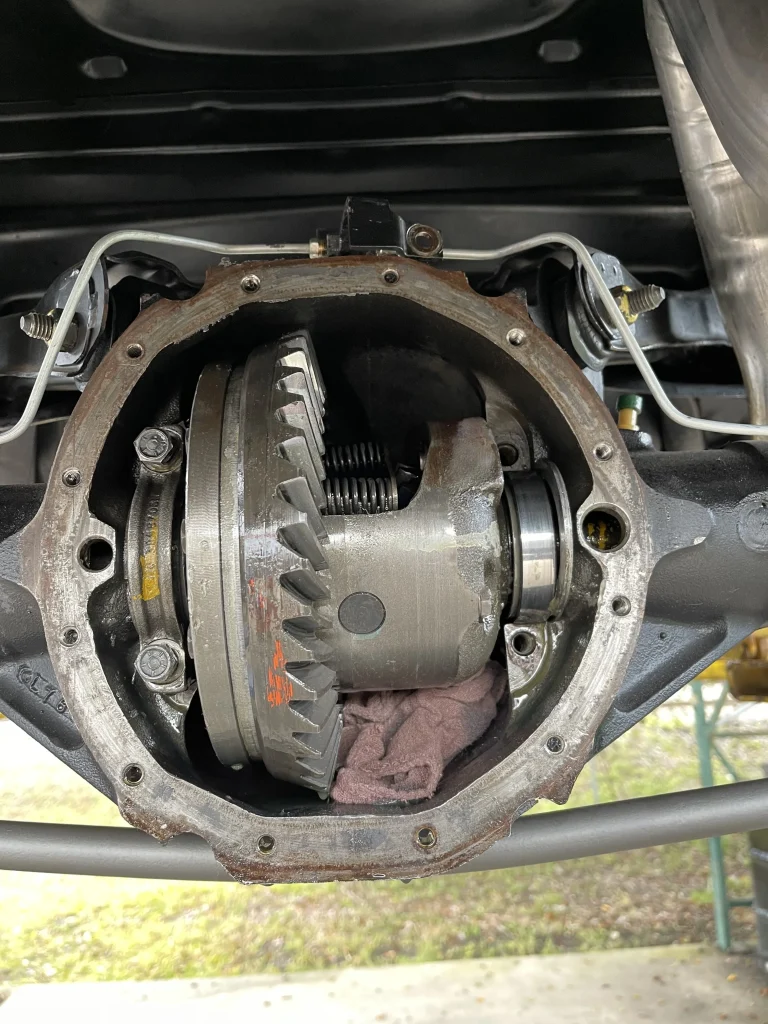
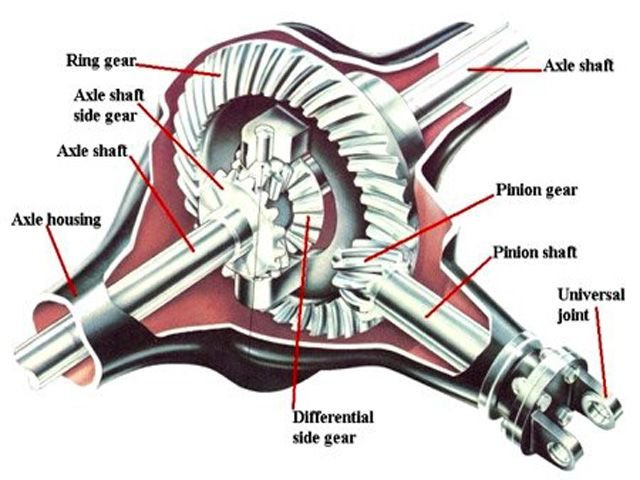
Before talking gear ratios, it’s important to understand what the rearend differential actually does. In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential splits the torque from the driveshaft between the two rear wheels. Its job includes:
-
Torque Distribution:
Allowing wheels to turn at different speeds when navigating corners. -
Power Multiplication:
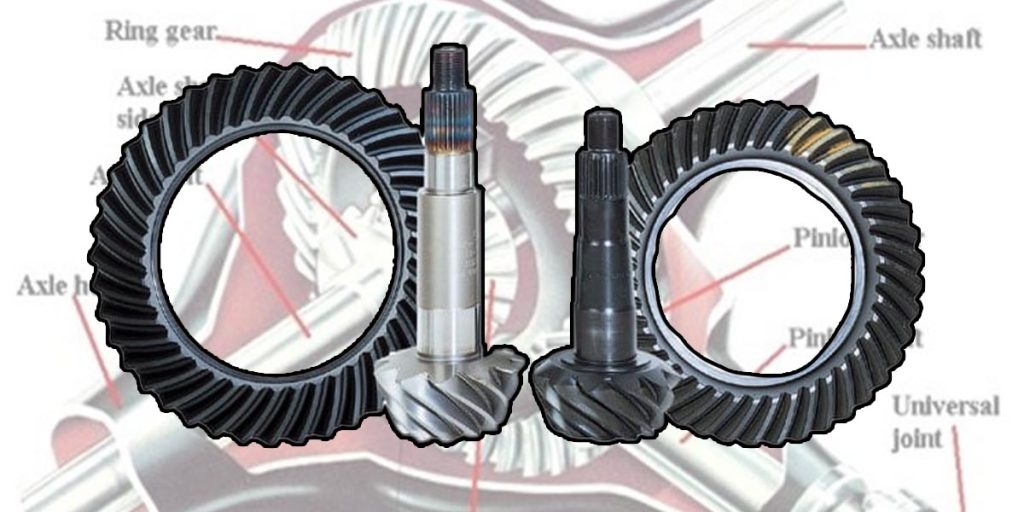
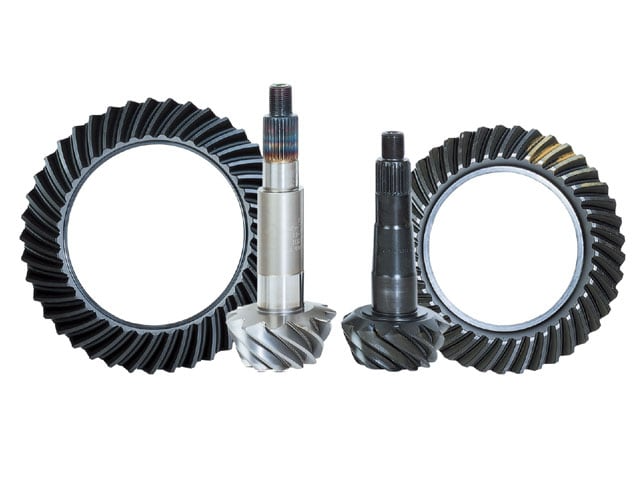
The interaction between the ring gear and the pinion gear creates a gear ratio that effectively multiplies engine torque before it reaches the wheels.
This ratio is expressed as a simple number (e.g., 3.73:1) that describes how many times the driveshaft rotates for each complete turn of the wheels.
How Differential Gear Ratios Work
The ratio between the number of teeth on the ring gear and those on the pinion gear defines the differential gear ratio. For example, a 3.73:1 ratio means that the driveshaft turns 3.73 times for every one rotation of the rear wheels. The choice of gear ratio has direct implications on how power is delivered:
Higher Numerical Ratios (e.g., 4.10, 4.56):
These ratios provide greater torque multiplication. This results in faster acceleration because more engine revolutions are converted into wheel rotations in a way that emphasizes low-end torque. However, this comes at the cost of higher engine RPM at cruising speeds.Lower Numerical Ratios (e.g., 3.08, 3.23):
Lower ratios result in lower engine RPM for a given road speed, which can improve fuel economy and reduce engine wear during highway driving. The trade-off is that acceleration may feel less vigorous.
Impact on Performance
The gear ratio differences can be felt in a few different ways:
Acceleration:
Higher ratios increase acceleration by allowing the engine to be in a more favorable power band during initial movement.Top Speed and Fuel Efficiency:
Lower ratios reduce engine speed at cruising speeds, potentially increasing top speed and improving fuel economy.Torque Delivery:
The multiplication effect of a higher ratio means that even if the engine isn’t revving at high RPM, the wheels receive a substantial torque boost—ideal for heavy vehicles or drag racing scenarios.

Differences Between Gear Ratios
High Gear Ratios (e.g., 4.10:1, 4.56:1):
- Acceleration Focused: Increased torque multiplication results in quicker launches and brisk acceleration.
- High RPMs: At highway speeds, the engine revs significantly higher, which may lead to increased wear and reduced fuel economy.
- Application: Popular in drag racing, performance muscle cars, and vehicles with lower overall gearing.
Low Gear Ratios (e.g., 3.08:1, 3.23:1):
- Economy and Comfort: Lower engine RPMs at cruising speeds mean quieter operation and better fuel efficiency.
- Reduced Acceleration: Less torque multiplication can result in slower off-the-line acceleration.
- Application: Favored in vehicles where comfort, long-distance cruising, and fuel economy are prioritized.
Pros and Cons of Different Gear Ratios
High Gear Ratios
Pros:
- More Acceleration:
More torque is delivered to the wheels, resulting in a more responsive launch and quicker acceleration. - Better for Performance Applications:
Ideal for vehicles built for drag racing or aggressive driving, where rapid acceleration is key.
Cons:
- Increased Engine RPM at Highway Speeds:
Higher RPMs can lead to increased engine noise, reduced fuel efficiency, and accelerated wear. - Potential for Reduced Top Speed:
In some cases, the high RPM required at cruising speeds might limit the maximum achievable speed due to engine redline restrictions.

Low Gear Ratios
Pros:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency:
Lower engine speeds at cruising speeds result in better fuel economy and quieter operation. - Enhanced Longevity and Comfort:
Reduced engine stress and well-suited for daily driving and long-distance cruising.
Cons:
- Slower Acceleration:
The reduced torque multiplication may make the vehicle feel sluggish during initial acceleration. - Less Suitable for High-Performance Scenarios:
For racing or heavy towing applications, the lower ratio might not provide the necessary power.
Application Considerations
Choosing the right differential gear ratio depends largely on the vehicle’s intended use:
Daily Driving and Highway Cruising:
A lower gear ratio is often preferred to maximize fuel economy and ensure a comfortable, quiet ride. The reduced engine RPM at cruising speeds translates to less noise and lower wear.Performance and Racing:
A higher gear ratio is desirable when acceleration and high torque are needed, such as in drag racing or aggressive street driving. While this may lead to higher engine RPM and potentially lower top speeds, the performance gains at lower speeds are significant.Towing and Heavy-Duty Use:
Vehicles that require substantial torque for towing or hauling may benefit from a higher gear ratio. The increased torque delivery helps move heavier loads, though it may come with a penalty in fuel efficiency.Modifications and Custom Builds:
Enthusiasts who modify their vehicles often experiment with different ratios to fine-tune performance characteristics. It’s important to consider the overall drivetrain, tire size, and engine power curve when selecting a gear ratio.
Ultimately, choosing the right gear ratio is a balancing act that depends on the specific needs and driving style of the vehicle owner. Whether you’re building a high-performance drag car or seeking a comfortable, fuel-efficient ride for daily commuting, understanding the trade-offs between different differential gear ratios is key to making an informed decision.
If you need help on deciding what gear ratio to use in your classic Chevrolet or need parts for your rearend differential, give our friendly techs a call at (203) 235-1200 or hop on SS396.com!